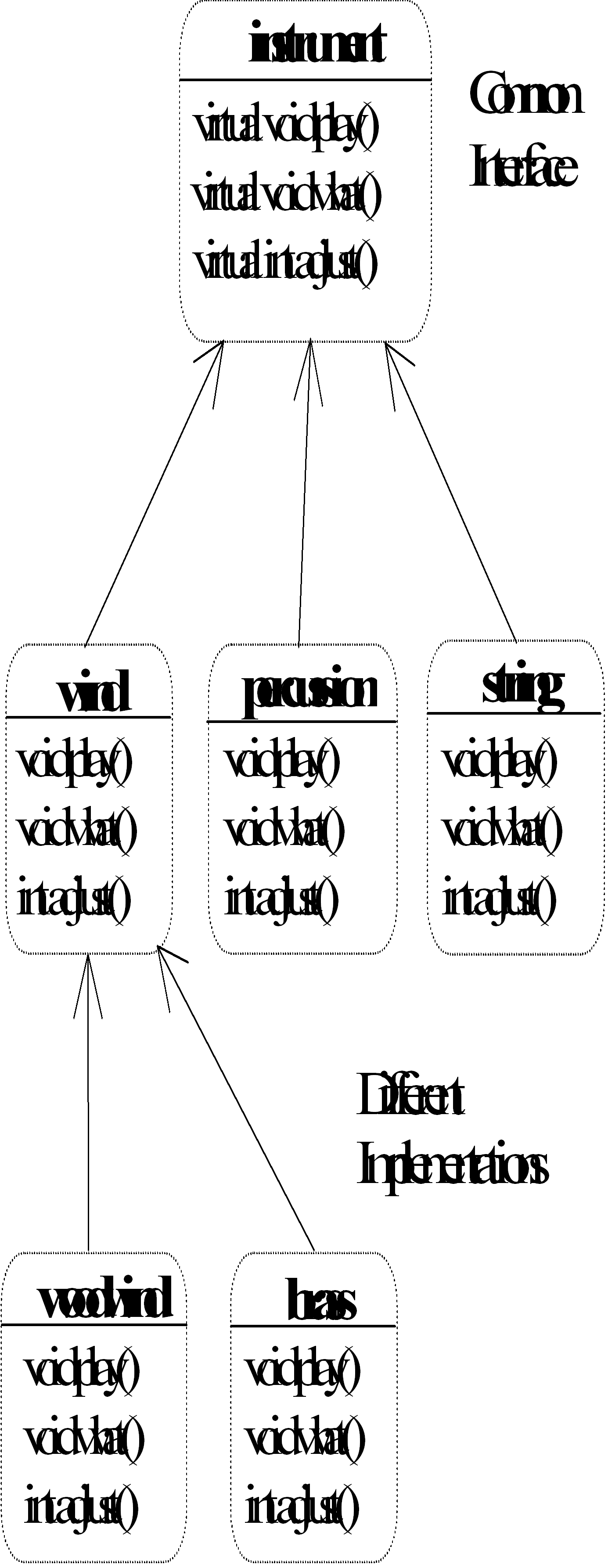
//: C15:Wind5.cpp
// Pure abstract base classes
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
enum note { middleC, Csharp, Cflat }; // Etc.
class Instrument {
public:
// Pure virtual functions:
virtual void play(note) const = 0;
virtual char* what() const = 0;
// Assume this will modify the object:
virtual void adjust(int) = 0;
};
// Rest of the file is the same ...
class Wind : public Instrument {
public:
void play(note) const {
cout << "Wind::play" << endl;
}
char* what() const { return "Wind"; }
void adjust(int) {}
};
class Percussion : public Instrument {
public:
void play(note) const {
cout << "Percussion::play" << endl;
}
char* what() const { return "Percussion"; }
void adjust(int) {}
};
class Stringed : public Instrument {
public:
void play(note) const {
cout << "Stringed::play" << endl;
}
char* what() const { return "Stringed"; }
void adjust(int) {}
};
class Brass : public Wind {
public:
void play(note) const {
cout << "Brass::play" << endl;
}
char* what() const { return "Brass"; }
};
class Woodwind : public Wind {
public:
void play(note) const {
cout << "Woodwind::play" << endl;
}
char* what() const { return "Woodwind"; }
};
// Identical function from before:
void tune(Instrument& i) {
// ...
i.play(middleC);
}
// New function:
void f(Instrument& i) { i.adjust(1); }
int main() {
Wind flute;
Percussion drum;
Stringed violin;
Brass flugelhorn;
Woodwind recorder;
tune(flute);
tune(drum);
tune(violin);
tune(flugelhorn);
tune(recorder);
f(flugelhorn);
} ///:~